How To Identify Zinc Fingers
Further the genes with these mutations also have high overall missense mutation rates are expressed at levels comparable to those of known cancer genes and together have biological. Originally the number and order of these residues was used to classify different types of zinc fingers eg Cys 2 His 2 Cys 4 and Cys 6.
 Exploring The Dna Binding Specificities Of Zinc Fingers With Dna Microarrays Pnas
Exploring The Dna Binding Specificities Of Zinc Fingers With Dna Microarrays Pnas
The complex at upper left PDB entry 1y0j shows zinc fingers from two longer proteins GATA-1 which contains two zinc fingers and FOG-1 which contains 9 zinc fingers.

How to identify zinc fingers. Design a Zinc Finger Protein Enter the DNA target site. Zinc finger tools are based on sequence pattern recognition which has the options of identifying zinc finger nuclease target sites and designing of zinc finger proteins. The stably folded structure consists of a beta strand-turn-beta strand-turn-alpha helix and is shown below 1zfn.
In general zinc fingers coordinate zinc ions with a combination of cysteine and histidine residues. Zinc has has an oxide that flakes off carrying some of the zinc so other things are coated in it so the zinc rusts instead of the base metal this is called galvanization. Zinc fingers are man-made molecules made of a protein and zincEach binds to a specific DNA.
Zinc is an important dietary nutrient that plays crucial roles throughout the entire body. They have two parts. ZIFIBI tool uses Hidden Markov Model HMM which is also used to identify the C 2 H 2 zinc finger target sites.
A zinc finger is a small functional independently folded domain that coordinates one or more zinc ions to stabilize its structure through cysteine andor histidine residues. Zinc-finger nucleases ZFNs are enzymes got by fusing a zinc finger to a DNA cleavage enzyme called a Fokl. This subsection of the Function section specifies the position s and type s of zinc fingers within the protein.
Zinc finger domains The DNA recognition sequence of each ZF usually corresponds to the N-terminal residues of the α-helix positions 1 to 6 relative to the start of the α-helix. The identity of the aminonoacids at the contact site defines. ZF Tools employs a non-redundant set of 49 helices to target as many DNA triplets 4 8.
The domain is typically 25-30 residues long and possesses two cysteine and two histidine residues that coordinate a zinc atom. However although using the Ecoli expression system the protein is soluble After gel filtration it is occuring in dynamic equilibrium state. As such zinc deficiency may cause hair loss 38 39 40.
Enter a DNA sequence to be scanned for target sites 10 kb max. By experimenting with zinc fingers Sangamo researchers were able to identify one specific splice variant of a protein called PPARgamma as the one responsible for making new fat cells. Zinc ribbons contain two zinc knuckles often β hairpins coordinating a zinc ion via a two Cys residures separated by 2-4 other residues on one knuckle and a Cys-x-x-Cys on the other Hahn and Roberts 2000.
Zinc fingers are domains known to bind nucleic acids and comprise a varied superfamily. The ZF amino acid sequence predicted to recognize this site. Functionally these motifs carry out a wide variety of tasks within cells by providing stable structural scaffolds and driving critical binding interactions especially among proteins DNA and RNA.
The specific interaction between these two zinc fingers plays an essential role in the development of blood cells. How may I be able to purify it. Zinc fingers are small compact protein subunits folding around chelated zinc ions.
Taking in too much zinc can be harmful however and it may cause a range of symptoms including nausea. The proteins encoded by nese52 and nele49 contain four C2H2 zinc-finger domains and share an amino acid identity of 356. Because of its low cost zinc is the main metal in us pennies.
Zincs melting point is 419C 786F. As the most common protein domain in the human genome C 2 H 2 zinc fingers C 2 H 2-ZF are known to espouse a wide variety of roles 13 involving the recognition and binding of both nucleic acids and proteins 46DNA binding is likely the most common because auxiliary DNA interacting domains including the potent transcriptional repressors KRAB and BTB 79 are often. Zinc is naturally dull grey and is very hard to polish.
This mineral is essential for protein synthesis and cell division two processes needed for hair growth. Zinc finger domains are very common with many thousands identified in many hundreds of proteins. The binding of a zinc-finger domain to its target site juxtaposes three base pairs on DNA to a few amino acids in the α-helix structure.
Numerous zinc finger genes are affected with those containing Krüppel-associated box KRAB repressor domains preferentially targeted by these mutations. More recently a more systematic method has been used to classify zinc finger proteins instead. Zinc finger nucleases or ZFN are a tool used to target genes and change DNAIt is one of three methods of changing the genome with engineered nucleases.
 Dna Conformation Induces Adaptable Binding By Tandem Zinc Finger Proteins Sciencedirect
Dna Conformation Induces Adaptable Binding By Tandem Zinc Finger Proteins Sciencedirect
 Design And Development Of Artificial Zinc Finger Transcription Factors And Zinc Finger Nucleases To The Htert Locus Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
Design And Development Of Artificial Zinc Finger Transcription Factors And Zinc Finger Nucleases To The Htert Locus Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
 Are Zinc Finger Nucleases Making A Comeback
Are Zinc Finger Nucleases Making A Comeback
 A Model Of The Site Specific Dna Recognition By S2n2 Zinc Finger Download Scientific Diagram
A Model Of The Site Specific Dna Recognition By S2n2 Zinc Finger Download Scientific Diagram
 Mutagenesis Induced By Zinc Finger Nuclease Activity A Cartoon Of Download Scientific Diagram
Mutagenesis Induced By Zinc Finger Nuclease Activity A Cartoon Of Download Scientific Diagram
 Zinc Finger Nucleases Induced By Hiv 1 Tat Excise Hiv 1 From The Host Genome In Infected And Latently Infected Cells Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
Zinc Finger Nucleases Induced By Hiv 1 Tat Excise Hiv 1 From The Host Genome In Infected And Latently Infected Cells Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
 The Dna Binding Domain Of The Nuclear Receptors A Diagram Of The Two Download Scientific Diagram
The Dna Binding Domain Of The Nuclear Receptors A Diagram Of The Two Download Scientific Diagram
 Selective Dimerization Of A C2h2 Zinc Finger Subfamily Molecular Cell
Selective Dimerization Of A C2h2 Zinc Finger Subfamily Molecular Cell
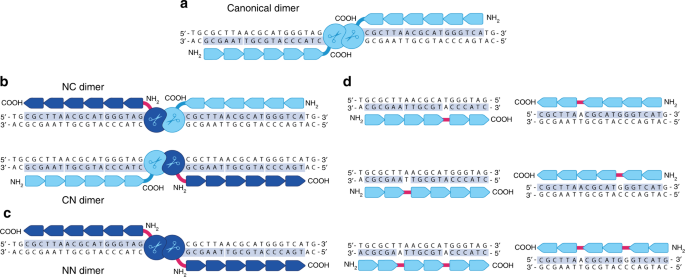 Diversifying The Structure Of Zinc Finger Nucleases For High Precision Genome Editing Nature Communications
Diversifying The Structure Of Zinc Finger Nucleases For High Precision Genome Editing Nature Communications
 Details Of Naturally Occurring Zinc Finger Proteins In Zif Base Download Table
Details Of Naturally Occurring Zinc Finger Proteins In Zif Base Download Table
 Differential Role Of Snail1 And Snail2 Zinc Fingers In E Cadherin Repression And Epithelial To Mesenchymal Transition Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Differential Role Of Snail1 And Snail2 Zinc Fingers In E Cadherin Repression And Epithelial To Mesenchymal Transition Journal Of Biological Chemistry
 Zinc Finger Protein An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Zinc Finger Protein An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Synthetic Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Action At An Endogenous Chromosomal Site Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Synthetic Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Action At An Endogenous Chromosomal Site Journal Of Biological Chemistry
 Highly Specific Zinc Finger Proteins Obtained By Directed Domain Shuffling And Cell Based Selection Pnas
Highly Specific Zinc Finger Proteins Obtained By Directed Domain Shuffling And Cell Based Selection Pnas
 C2h2 Zinc Finger Motif A The C2h2 Zinc Finger Motif 2 Cys And 2 His Download Scientific Diagram
C2h2 Zinc Finger Motif A The C2h2 Zinc Finger Motif 2 Cys And 2 His Download Scientific Diagram
 Tumor Associated Zinc Finger Mutations In The Ctcf Transcription Factor Selectively Alter Its Dna Binding Specificity Cancer Research
Tumor Associated Zinc Finger Mutations In The Ctcf Transcription Factor Selectively Alter Its Dna Binding Specificity Cancer Research
 Protein Delivery Of Cell Penetrating Zinc Finger Activators Stimulates Latent Hiv 1 Infected Cells Molecular Therapy Methods Clinical Development
Protein Delivery Of Cell Penetrating Zinc Finger Activators Stimulates Latent Hiv 1 Infected Cells Molecular Therapy Methods Clinical Development
 Expanding The Repertoire Of Target Sites For Zinc Finger Nuclease Mediated Genome Modification Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
Expanding The Repertoire Of Target Sites For Zinc Finger Nuclease Mediated Genome Modification Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
 Sticky Fingers Zinc Fingers As Protein Recognition Motifs Trends In Biochemical Sciences
Sticky Fingers Zinc Fingers As Protein Recognition Motifs Trends In Biochemical Sciences